목차
Algebra of Sets (집합의 대수학)
대수학이란? 일련의 공리들을 만족하는 수학적 구조들의 일반적인 성질을 연구하는 수학의 한 분야 (위키백과) 를 의미한다. 집합의 대수학이라 함은 집합이라는 대상과, 집합이 만족하는 성질들에 대한 학문을 의미할 것이다.
universal set : 상상할 수 있는 모든 요소의 집합 (set of all elements under consideration)
subset : \(A \subset B\) 이면 A는 B의 Subset 부분집합 이라고 한다.
empty set : 아무런 요소가 없는 집합. 공집합 \( \phi \)
complement : \(A^c\) Set of points that are in S but not in A
union : \( A \cup B\) set of points that are in A or B
intersection : \(A \cap B\) set of points that are in both A and B
mutually exclusive (disjoint) : If \(A \cap B = \phi\) then, A and B are mutually exclusive (=disjoint)
laws
Commutative laws : 교환 법칙 \(A \cup B = B \cup A\)
Associative laws : 결합 법칙 \(A\cap(B \cap C) = (A \cap B) \cap C\)
Distributive laws : 분배 법칙 \(A\cap(B \cup C) = (A\cap B) \cup (A\cap C)\)
DeMorgan's laws : 드모르간의 법칙 \((A \cap B)^c = A^c \cup B^c\)
Basics of Probability Theory
A random experiment (3 conditions)
- 모든 가능한 결과가 알려져있다. (all possible outocomes of the experiment are known.)
- 결과 예측을 할 수 없어야 한다. (the outcome can't be predicted with cerntainty before the experiment is performed.)
- 동일조건 하 반복가능해야 한다. (the experiment can be repeated under indentical conditions.)
기본 용어 및 개념
Sample Space : Set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment
Event : subset of sample space
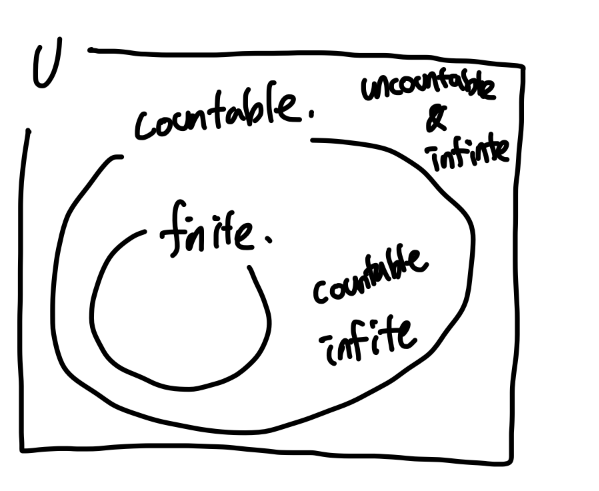
Discrete sample space (tossing a die) : the number of element of sample space is countable ( finite or infinitely countable) : 각 Event에 확률을 할당 할 수 있음
Continuous sample space (random select from the interval) : the number of element of sample space is uncountable : Compound events (interval)에 확률을 할당함. 각 Event에 확률을 할당할 수 없음 (할당하는 순간 P의 합은 발산함 -> Normalization 위배)
Function \(f(x) : A \to B\) : assign each \(x \in A\) to an unique element \(f(x) \in B\)
- Domain : A 정의역
- Range : set of output values f(x) 치역
- Real valued function : Range is real number set
- Set function : Domain이 collection of sets 인 Real valued function
Axiom of probability (kolmogorov)
: 확률(Probability)은 Set function이다. Sample Space 가 정의역 (Event A의 집합) , Range 는 [0,1] 구간의 실수. 아래 세 조건을 만족시키면 확률이다.
- \(P(A) \geq 1 \)
- \(P(S) = 1\)
- Countable Additivity \[P\left [ \bigcup_{i = 1}^{\infty}A_i\right ] = \sum_{i=1}^{\infty}P(A_i)]\
확률의 몇가지 성질들
- \(P(A^c) = 1 - P(A)\)
- \(P(\phi) = 0\)
- \(A \subset B \to P(A) \leq P(B)\)
- \(P(A\cup B ) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \cap B)\)
- Inclusive-Exclusive formula \[P(A\cup B\cup C) = P(A)+P(C)+P(C)-P(A\cap B)-P(B\cap C)-P(A\cap C)+P(A\cap B\cap C) ]\
Methods of Enumeration
Equally Likely : 각 Event의 확률이 모두 같을 때(same P of occuring) Equally Likely라고 한다. \[P(A) = \frac{k}{n} = \frac{N(A)}{N(S)}\]
Multiplication rule : 곱의 법칙 (two coins , two dices : 경우의수는 (2)(2)(6)(6))
Ordered sample : order of selection is noted. 뽑는 순서가 있다.
With replacement : 복원. 공을 뽑아 확인한 뒤 다시 항아리에 넣어 두는 경우.
Sampling의 종류 (4가지 + a)
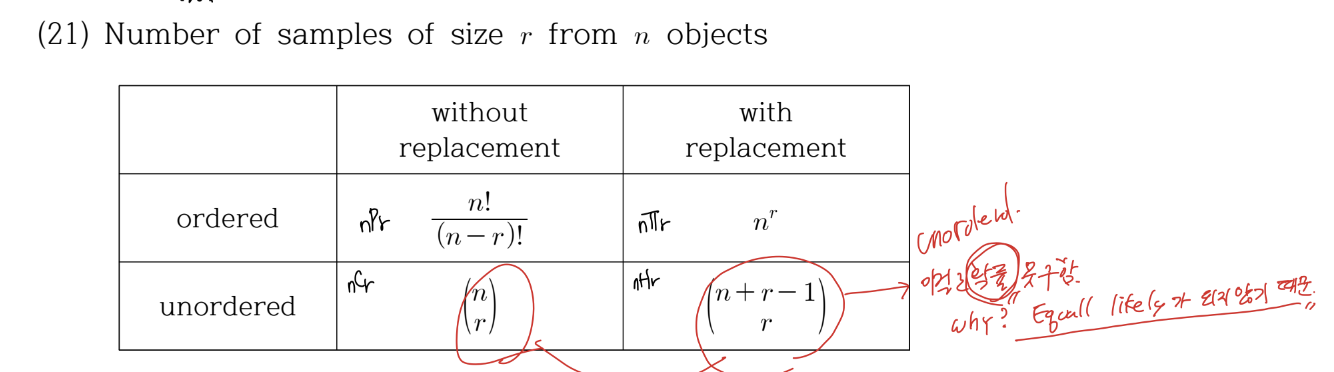
Sampling without Replacement Ordered (순열) : Permutation \(_{n}P_{r} = \frac{n!}{(n-r)!} \)
Sampling with Replacement Ordered(중복순열) : \(n^r\)
Birthday problem : 한 반에 r명의 학생이 있을 때, 모두 생일이 다를 확률 (2월 29일생, 윤년 고려 X) \[ \left ( 1-\frac{1}{365} \right )\times\left ( 1-\frac{2}{365} \right )\times ... \times \left ( 1-\frac{r-1}{365} \right ) = \prod_{r-1}^{k =1}\left ( 1-\frac{k}{365} \right ), r \geq 2\]
Sampling without Replacement Unordered(조합) : Combination
\(_{n}C_{r}=\frac{n!}{(n-r)! r!}=\binom{n}{r}\)
Binomial theorem : \((x+y)^n = \sum_{r = 0}^{n}\binom{n}{r}x^r y^{n-r}\)
urn contains 5 red, 3 green, 2 blue and 4 white balls. sample of size 8 is selected at random without replacement. The probability that sample contain (2,2,1,3)
- \[\frac{\binom{5}{2}\binom{3}{2}\binom{2}{1}\binom{4}{3}}{\binom{14}{8}}]\
\((1-1)^n \) and \((1+1)^n\)
- \((1-1)^n = \sum_{r=0}^{n}\binom{n}{r}(-1)^r = 0\)
- \((1+1)^n = \sum_{r=0}^{n}\binom{n}{r} = 2^n\)
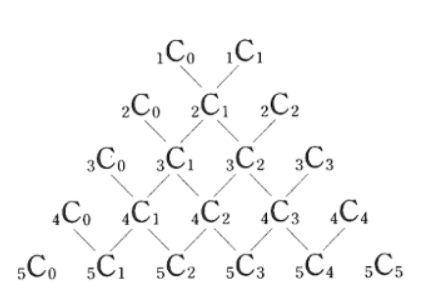
Pascal's Triangle : N명 중에 r명이 총에 맞는다 하자. 전체 sample space는 두개로 분류할 수 있다. 내가 걸리느냐 안걸리느냐. 내가 걸리지 않는 경우의 수는 다시말해 나 빼고 N-1명중 r 명을 고르는 경우의 수이므로 \(\binom{n-1}{r}\) 이다. 내가 걸리는 경우의 수는, 다시 말해 나를 뽑은 상태에서 남은 n-1명 중 r-1명을 뽑는 경우의 수이므로 \(\binom{n-1}{r-1}\)이다. 즉 \(\binom{n}{r} = \binom{n-1}{r} + \binom{n-1}{r-1}\) 이다.
- 여기서 n과 r에 차례대로 0부터의 수를 대입해보면 아래 파스칼의 삼각형이 나온다.
Distinguishable Permutation (같은 것이 있는 순열) : 공이 총 n개가 있는데 같은 종류의 공이 각각 r1개, r2개 ,... , rk개 가 있다. \(r_1 + r_2 _+ ... + r_ k = n\) 이때, Distinguishable permutation은 전체 배열의 경우의 수 n! 에서 각각의 같은 종류 애들에 의한 구분을 없애줘야 하므로 \(\frac{n!}{r_1! \cdot r_2! \cdot ... \cdot r_k !}\)
- multi-nomial expansion : 위의 \(\frac{n!}{r_1! \cdot r_2! \cdot ... \cdot r_k !}\)이 부분은 사실 우리가 자주 볼 수 있다. 바로 여러 항의 합의 n승 꼴의 전개식에서 말이다. \[(x_1 + x_2 + ... + x_k)^n = \sum(\frac{n!}{r_1! \cdot r_2! \cdot ... \cdot r_k !})x_{1}^{r_1}x_{2}^{r_2}...x_{k}^{r_k}]\
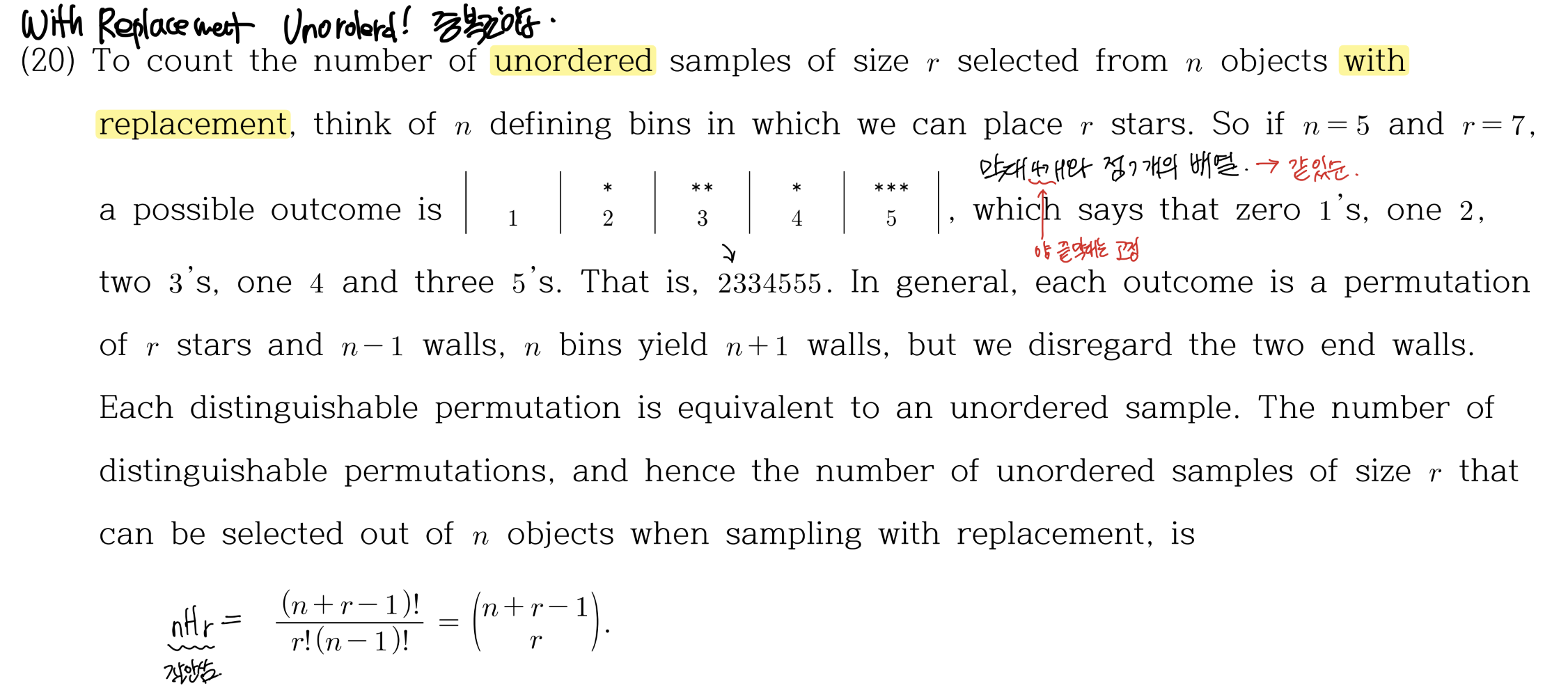
Sampling with Replacement Unordered (중복조합)
\(x + y + z = 10 \) x,y,z는 정수 ... 이런 문제에서 자주 본 중복조합. 보통 막대기와 공의 배열로 설명을 한다. 우리가 총 n개의 구별되는 구슬이 있고, 중복을 허용해 r번 뽑은 뒤 각각의 공이 총 몇번 뽑혔는지 기록한다고 하자. 이 기록의 경우의 수는 다시 r이라는 수를 n등분 (0개도 하나의 등분으로 포함) 하는 경우의 수다. 막대 n-1개와 공r개를 나열하는 경우의 수와 같다. r개와 n-1개가 각각 구분이 되지 않는 distinguish permutation 이므로, 이 경우의 수는 \(\binom{n+r-1}{} = \frac{(n+r-1)!}{(n!)(r-1)!}\)이다. 참고로 nHr 이라는 식은 해외에서는 잘 쓰이지 않고 한국과 일본에서만 쓰인다고 한다.
Equally Likely 하지 않은 경우의 확률은 각각 구해준다
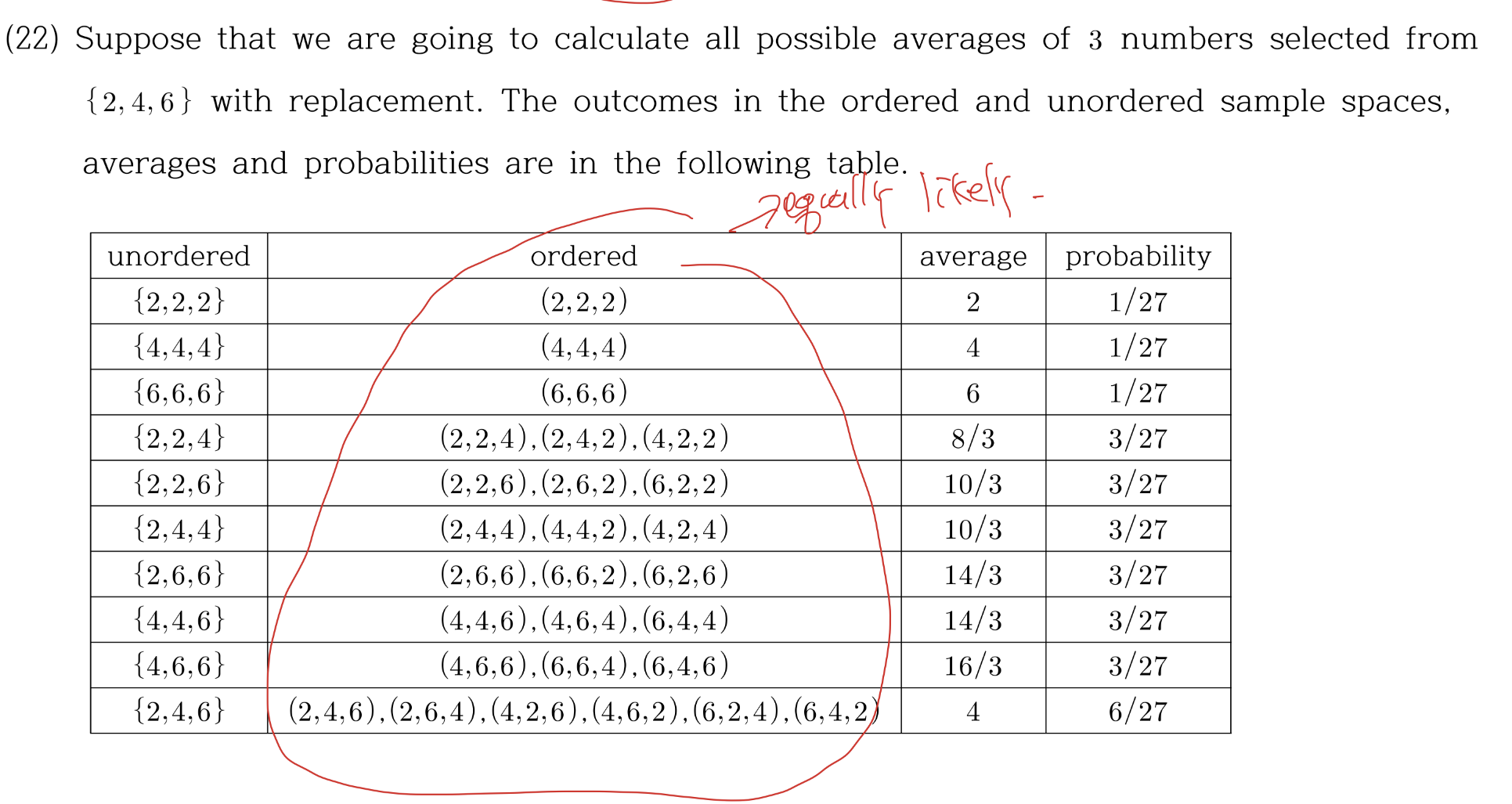
2,4,6 중에 with replacement로 세번 샘플링 한다 치자. 우리가 (2,4,4)라는 이벤트의 확률과 (2,4,6)라는 이벤트의 확률은 같지 않다. 즉 sample space의 각 event 들의 확률이 다르므로 equally likely 하지 않다. 이럴 경우에 이 친구들의 확률 계산을 sample space에서 하면 틀리게 된다. 각 event의 확률을 각각 계산해야한다.
Conditional Probability
Conditional Probability
B가 발생했을때의 A의 확률 : \(P(A|B) = \frac{P(A \cap B)}{P(B)}\)
three axioms
- \(P(A|B) \geq 0 \)
- \(P(S|B) = 1\)
- Mutually exclusive한 A들에 대해서,\(P \left [\bigcup_{i=1}^{\infty} A_i |B \right ] = \sum_{i=1}^{\infty}P(A_i|B)\)
Multiplication rule (조건부확률의 곱의 법칙)
\[P(A\cap B) = P(B) P(A|B) = P(A)P(B|A)\]
2개에 대해서 되면 N개에 대해서도 항상 된다! (김주한 교수 曰) 수식 길어서 사진으로 대체. 순서에 집중해서 외우기. A1,A2,A3에 대해서는, \(P(A_1) P(A_2|A_1)P(A_3|A_1 \cap A_2)\)

Independant Events
"확률적" 독립이란
Independant : 확률 구조상 독립이라는 거지, 두 대상이 의미적으로 독립이라는 것은 아니다. 실제로 연관이 있더라도, 확률 구조상 독립일 수도 있다. 다만 실제로 독립이라면, 확률적으로도 독립일 것이다.
\[P(A) = P(A|B) , P(B) = P(B|A)\]
\[P(A\ cap B) = P(A) P(B) \]
If A and B is independant, following three are independant
- \(A, B^c\)
- \(A^c, B\)
- \(A^c , B^c\)
If \(A_1, A_2 , ... , A_n\) are independant
둘둘 쌍(pairwise) 부터 N개끼리 모두 독립이어야 독립이다.
- pair-wise independant : \(P(A_i \cap A_j) = P(A_i)P(A_j)\)
- \(P(A_i\cap A_j \cap A_k) = P(A_i)P(A_j)P(A_k)\) 이 것이 3개, 4개 ... n 개 대해 모두 성립
pairwise 하다고 독립은 아니지만, 독립이면 pairwise 하다. (independant imply pairwise independant, but pairwise independant doesn't imply independant)
Bayes' Theorem
Partition
다 더하면 전체집합인데, 교집합이 하나도 없을때. 마치 세포분열한 colony같이 분할 될때 이를 Partition이라 한다.
Total Probability theorem
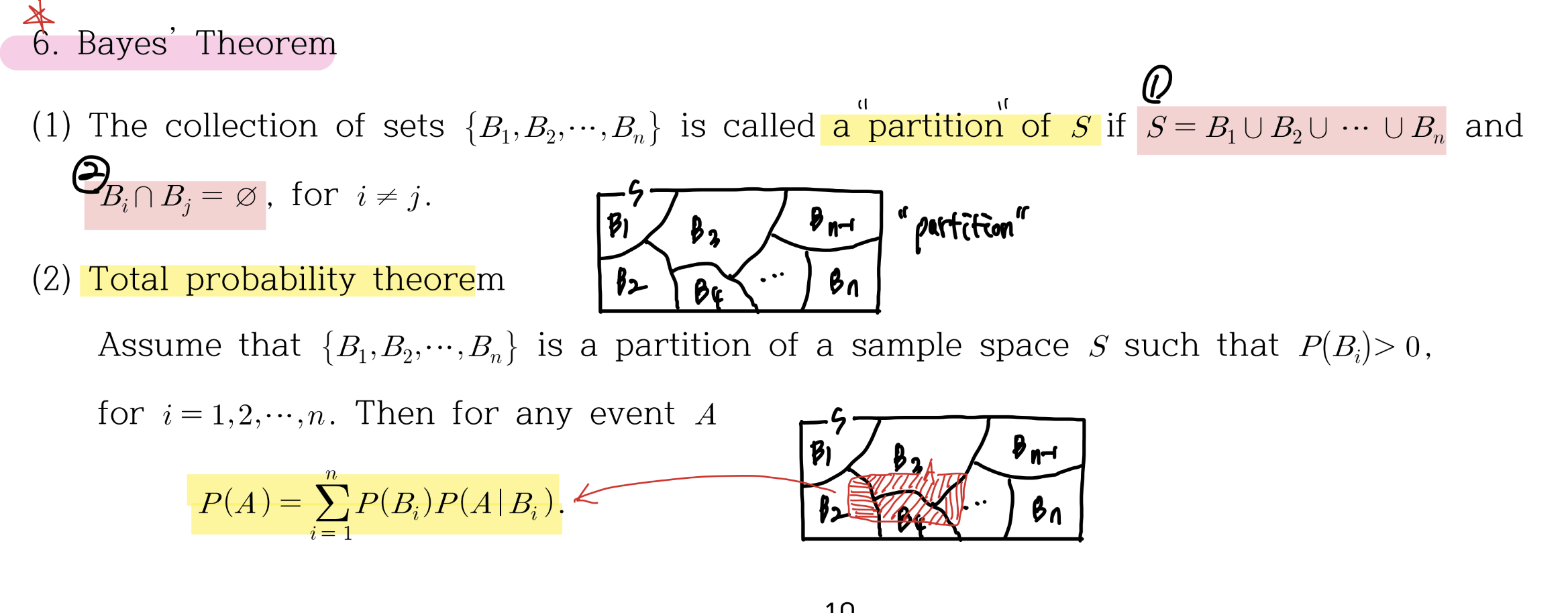
\[P(A) =P(A \cap B_1) + P(A \cap B_2) + ... = \sumP(B_i)P(A|B_i)\]
Bayes' theorem (how to calculate the posterior probability)
앞서 Total Probability Theorem은 \(P(A|B_k)\)를 갖고 P(A)를 구하는 방법에 대한 공식이었다면, 이번 Bayes' Theorem은 \(P(B_k|A)\)를 구하는 방법에 대한 식이다.
A라는 사건 위에서 B의 비율을 구해야하므로, 당연히 분모에 A의 확률이 들어가고, 분자에는 둘의 교집합이 올라가야한다. 이때 분모의 P(A)는 위에서 구한대로 TPT를 이용해 구하고, 분자의 P(A)는 Conditional Probability의 정의에 의해 구한다.
\[P(B_k|A) = \frac{P(B_k \cap A)}{P(A)} = \frac{P(B_k)P(A| B_i)}{\sum{P(B_i)P(A|B_i)}} \]
여기서 \(P(B_k)\)는 A가 일어나기 전의 확률이라는 의미에서 prior probability 라고 부르고,\(P(B_k|A)\)는 A가 일어난 이후 B의 확률이라는 점에서 posterior probability 라고 부른다.
EX) Urn i = i개의 defective 공 , 10 - i개의 정상 공. i = 1 to 5
(1) defective 공이 걸릴 확률 : P(A) -> Total Probability Theorem
Event A 는 defective ball 이 걸릴 확률이다. Partition을 먼저 생각해보면, 전체 Sample space를 5개의 event (1번 urn select , 2번 urn select , ... , 5번 urn select) 가 partition을 이루고 있다.
\[P(A) = \sumP(B_i)P(A|B_i) = \sum \frac{1}{5} \frac{i}{10} = \frac{3}{10}\]
(2) defective 공일 때, 그게 Urn 5에서 나온 것일 확률
\[P(B_5|A) = \frac{P(B_5)P(A|B_5)}{P(A)} = \frac{1/5 \times 5/10}{3/10} = 1/3\]
'Math > 확률과 통계 Probability and Statistics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [3-1~4-2] Discrete and Continuous Distribution (0) | 2023.03.25 |
|---|---|
| [2-1/2-2] Discrete Distribution, pmf, moment, mgf (0) | 2023.03.12 |


댓글